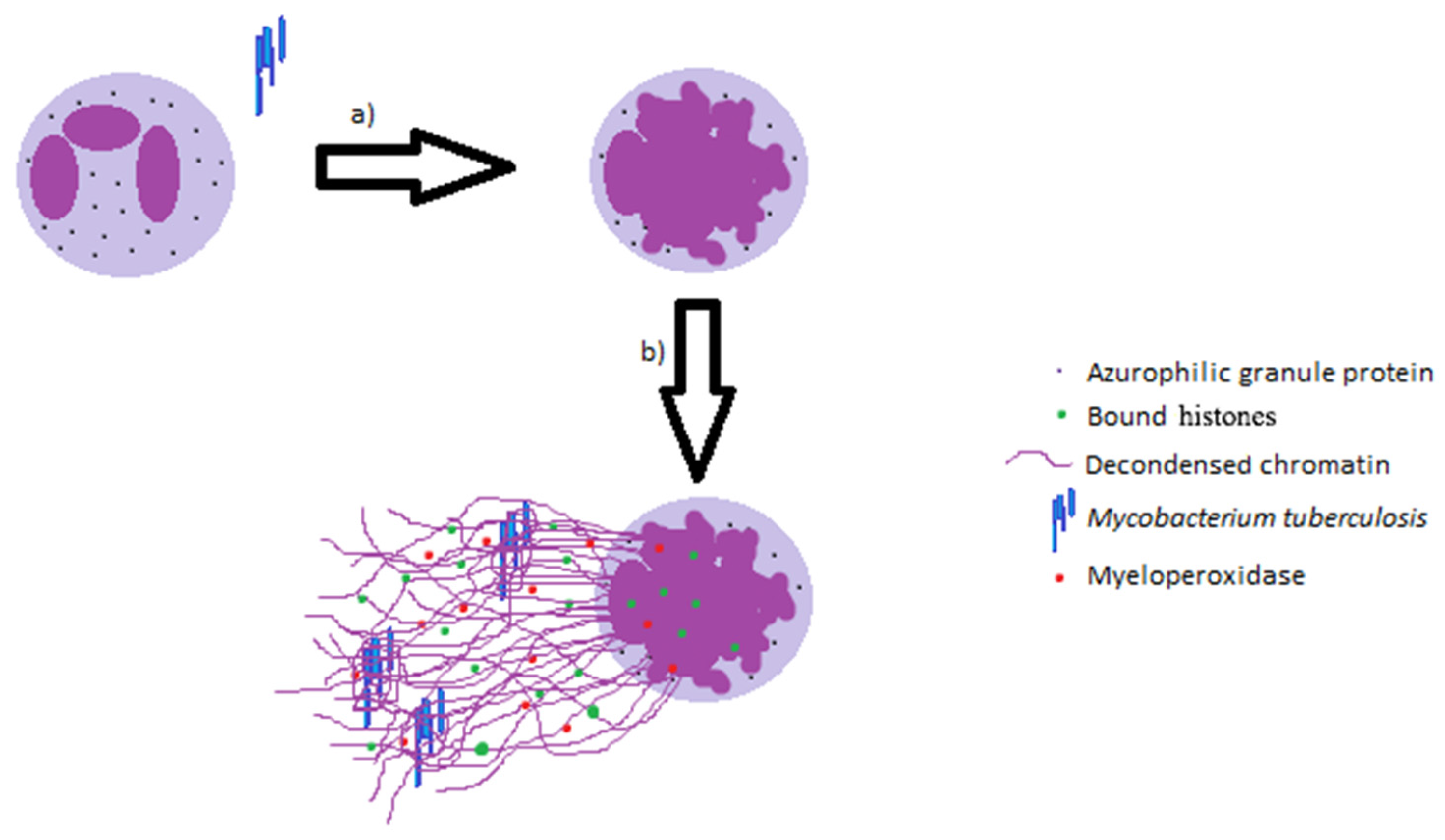
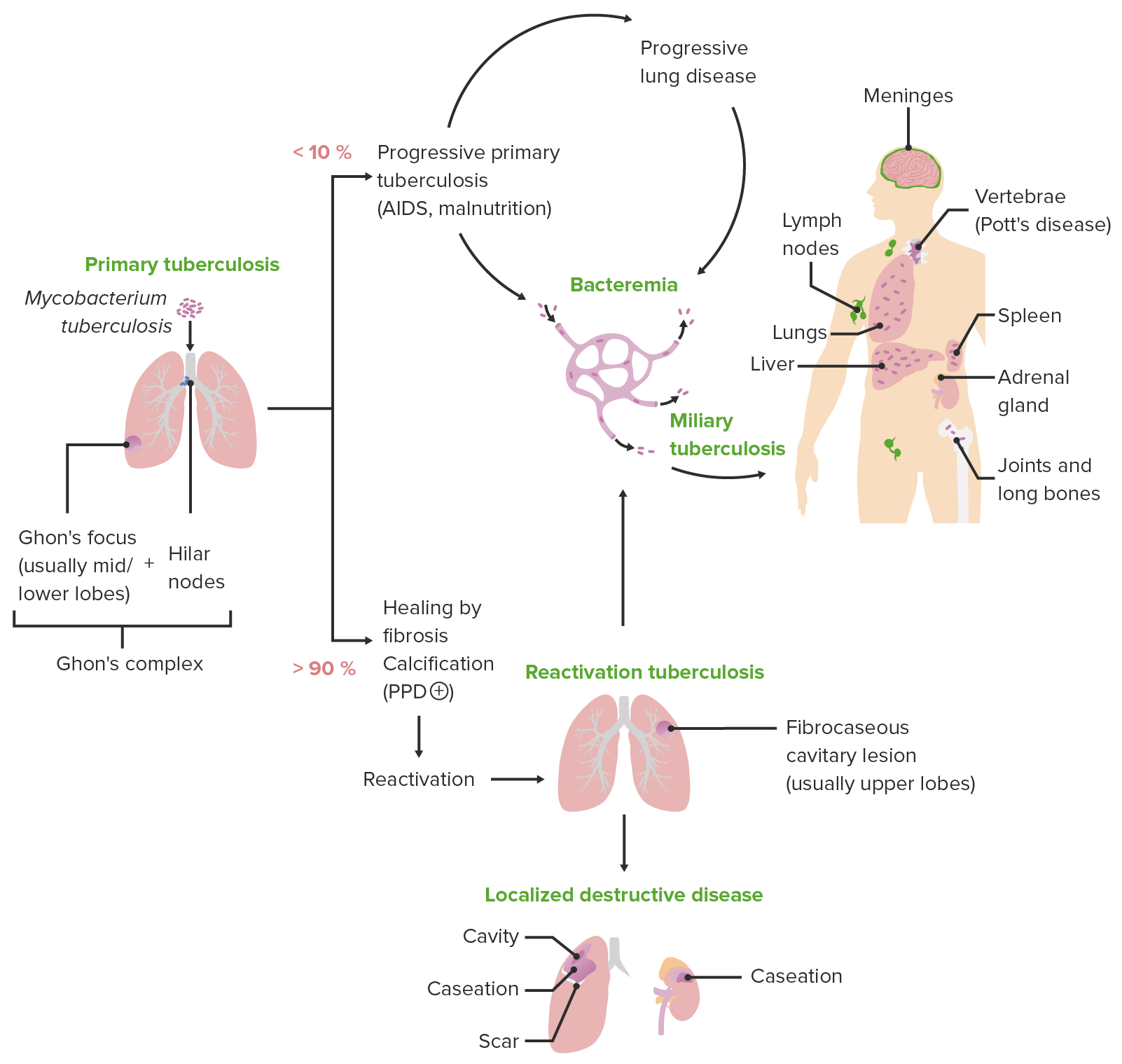
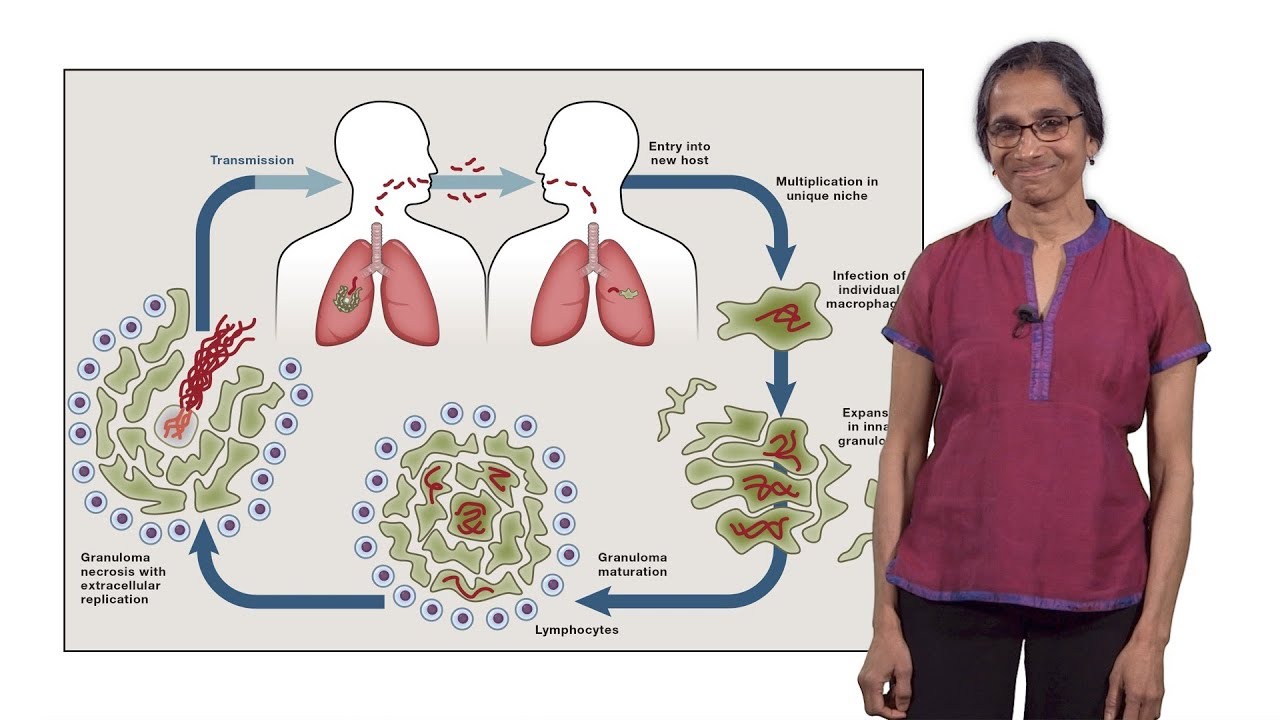
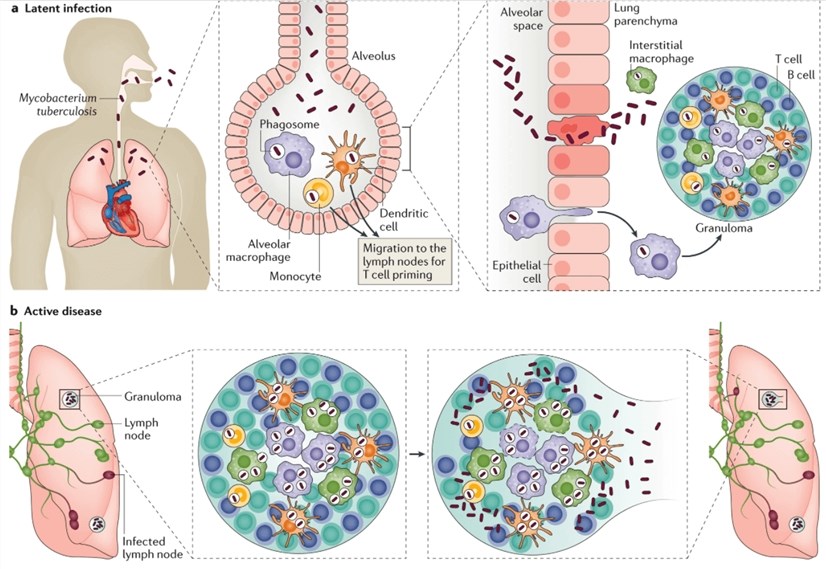
The mechanisms and consequences of the extra-pulmonary dissemination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis - ScienceDirect

Protection against tuberculosis: cytokines, T cells, and macrophages | Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases

Mode of action of Mtb and mechanism of developing active TB disease.... | Download Scientific Diagram
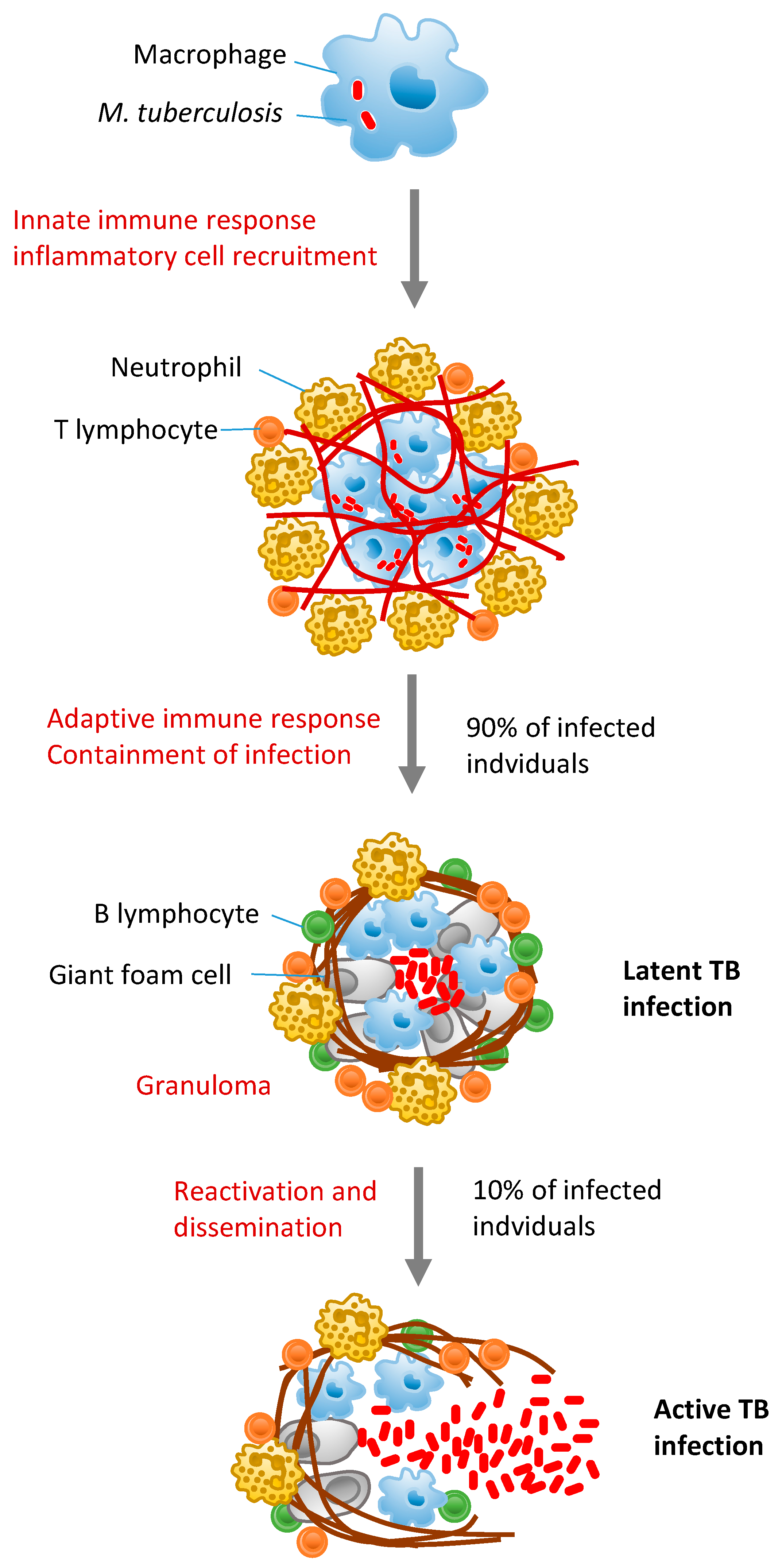
Cells | Free Full-Text | Tuberculosis-Associated MicroRNAs: From Pathogenesis to Disease Biomarkers | HTML

The Echo of Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Mechanisms of Clinical Symptoms and Other Disease-Induced Systemic Complications | Clinical Microbiology Reviews

Opening Pandora's Box: Mechanisms of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Resuscitation: Trends in Microbiology
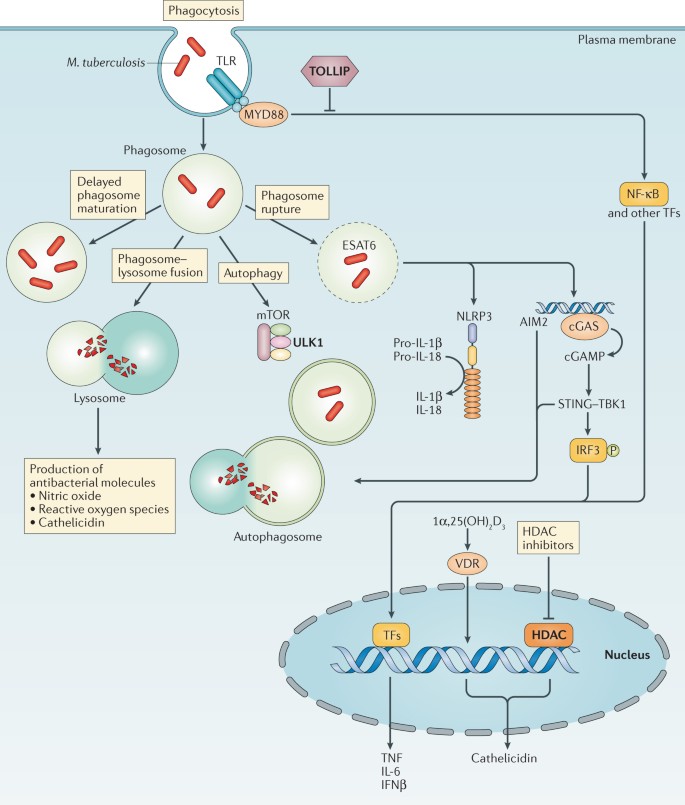
Immunological mechanisms of human resistance to persistent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection | Nature Reviews Immunology

Fig. 2.3, Schematic representation of basic immunological antimycobacterial mechanisms in the lung and lymphnode. Macrophages and dendritic cells initially encounter Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.TB) in the lung. A After ingestion, macrophages can undergo

Pathogenesis of tuberculosis. TB pathogenesis can be divided in four... | Download Scientific Diagram
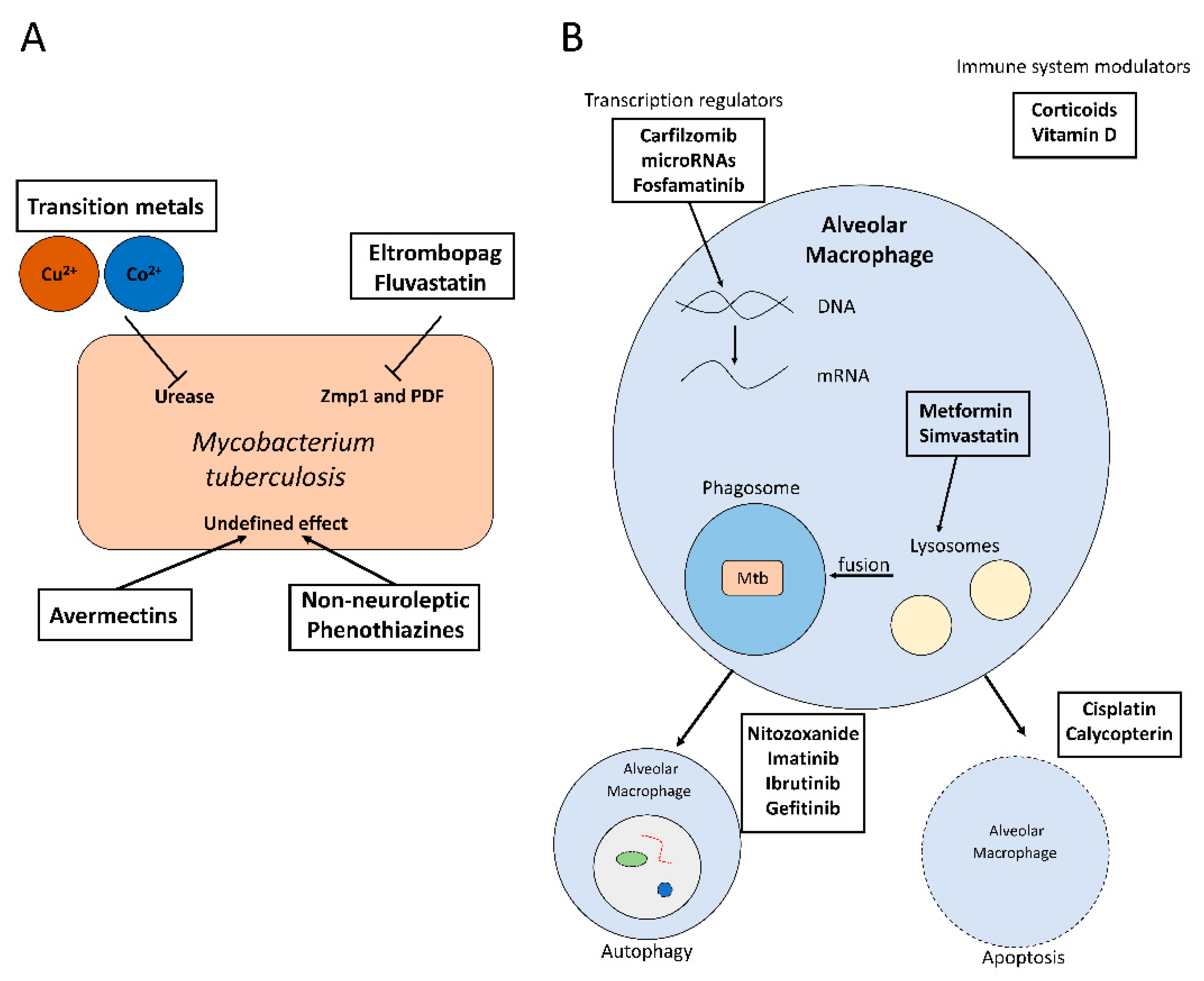
Antibiotics | Free Full-Text | Novel Treatments against Mycobacterium tuberculosis Based on Drug Repurposing | HTML

Latent tuberculosis: mechanisms of host and bacillus that contribute to persistent infection - The Lancet Infectious Diseases